10 March 2024
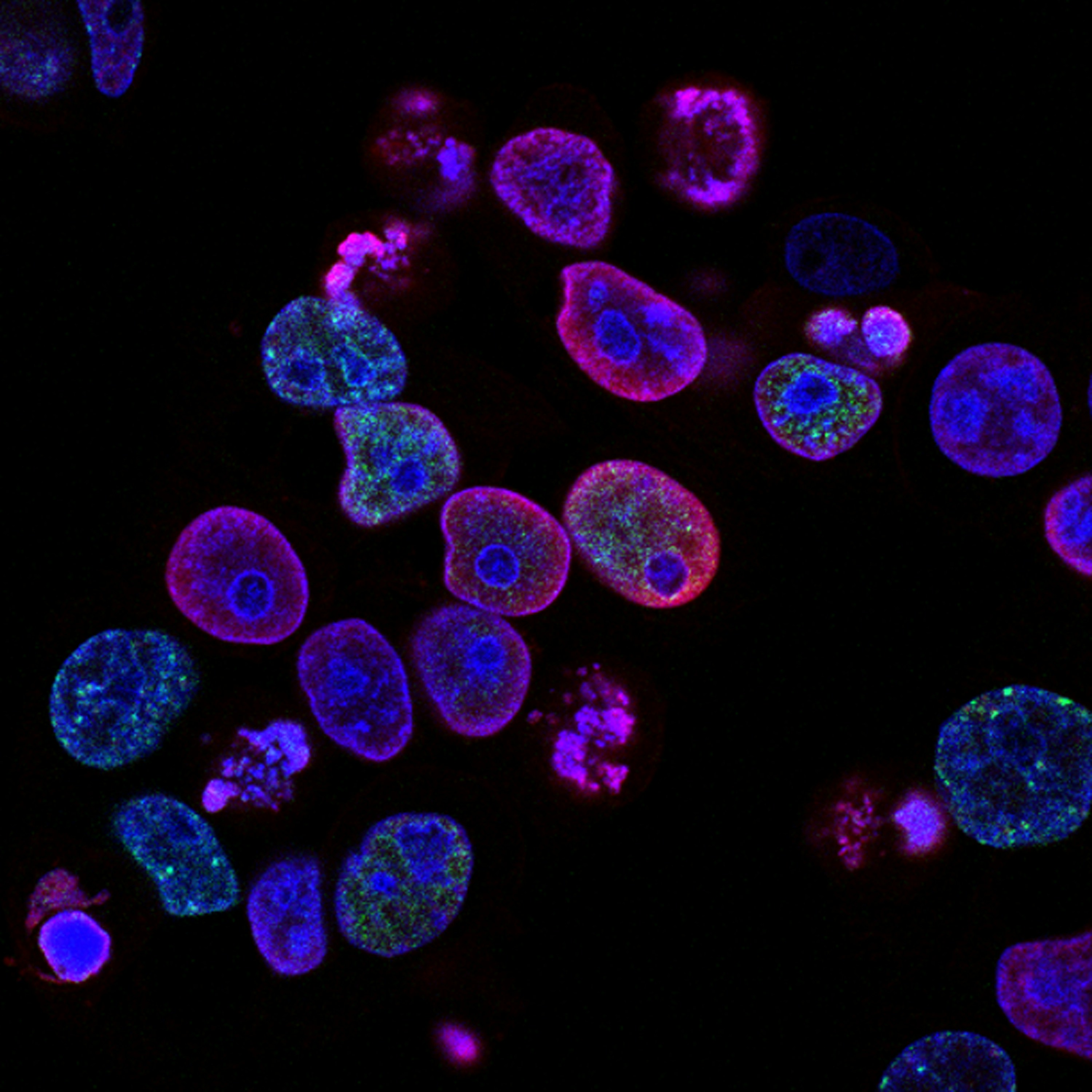
Immunotherapy is revolutionizing cancer treatment by harnessing the body's immune system to fight cancer cells. Unlike traditional therapies like chemotherapy and radiation, which target cancer directly but can also harm healthy cells, immunotherapy enhances the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells specifically.
There are several types of immunotherapy, including checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T cell therapy, and cancer vaccines. Checkpoint inhibitors block proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells, effectively "releasing the brakes" on the immune response. CAR-T cell therapy involves modifying a patient's T-cells to better recognize and kill cancer cells. Cancer vaccines stimulate the immune system to attack specific cancer-related antigens.

Immunotherapy has shown remarkable success in treating various cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer, and leukemia. Patients who previously had limited treatment options are experiencing significant improvements and, in some cases, long-term remission. Researchers continue to explore new combinations of immunotherapy with other treatments to enhance its effectiveness.
Despite its promise, immunotherapy is not without challenges. Some patients experience immune-related side effects, and not all cancers respond equally to treatment. Ongoing research aims to understand why certain cancers are resistant and how to overcome these barriers.
Play video
More stories
10 March 2024

Immunotherapy is revolutionizing cancer treatment by harnessing the body's immune system to fight cancer cells. Unlike traditional therapies like chemotherapy and radiation, which target cancer directly but can also harm healthy cells, immunotherapy enhances the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells specifically.
There are several types of immunotherapy, including checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T cell therapy, and cancer vaccines. Checkpoint inhibitors block proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells, effectively "releasing the brakes" on the immune response. CAR-T cell therapy involves modifying a patient's T-cells to better recognize and kill cancer cells. Cancer vaccines stimulate the immune system to attack specific cancer-related antigens.

Immunotherapy has shown remarkable success in treating various cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer, and leukemia. Patients who previously had limited treatment options are experiencing significant improvements and, in some cases, long-term remission. Researchers continue to explore new combinations of immunotherapy with other treatments to enhance its effectiveness.
Despite its promise, immunotherapy is not without challenges. Some patients experience immune-related side effects, and not all cancers respond equally to treatment. Ongoing research aims to understand why certain cancers are resistant and how to overcome these barriers.
Play video
More stories
10 March 2024

Immunotherapy is revolutionizing cancer treatment by harnessing the body's immune system to fight cancer cells. Unlike traditional therapies like chemotherapy and radiation, which target cancer directly but can also harm healthy cells, immunotherapy enhances the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells specifically.
There are several types of immunotherapy, including checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T cell therapy, and cancer vaccines. Checkpoint inhibitors block proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells, effectively "releasing the brakes" on the immune response. CAR-T cell therapy involves modifying a patient's T-cells to better recognize and kill cancer cells. Cancer vaccines stimulate the immune system to attack specific cancer-related antigens.

Immunotherapy has shown remarkable success in treating various cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer, and leukemia. Patients who previously had limited treatment options are experiencing significant improvements and, in some cases, long-term remission. Researchers continue to explore new combinations of immunotherapy with other treatments to enhance its effectiveness.
Despite its promise, immunotherapy is not without challenges. Some patients experience immune-related side effects, and not all cancers respond equally to treatment. Ongoing research aims to understand why certain cancers are resistant and how to overcome these barriers.
Play video